Home
Product Manager in 2024: Defintion, Key-Skills, Tips & Career Insights
Unlock the secrets to becoming a successful Product Manager—from essential skills to career growth paths and insider tips for breaking into the field!
CHRISTIAN CASSISI – 11/09/2024

Product Manager at leading his Product Team / Pexels.com / fauxels
What is Product Management |
Importance of Product Management in Modern Business |
Key Roles & Responsibilities of Product Managers |
Essential Skills for Product Managers|
Common Product Management Frameworks and Tools|
Career Path & Grwoth Opportunities |
Key Skills for a Career in Product Management |
How to Become a Product Manager|
Salary & Job Outlook|
In today’s fast-paced, digital-first world, the role of a product manager has become indispensable for modern businesses. But what exactly does a product manager do, and why are they crucial to a company’s success? This guide unpacks the evolving role of product managers, their responsibilities, and why they hold such a pivotal position in product-driven companies.
What is Product Management?
Product management is the process of guiding the success of a product, from initial conception to final launch and beyond. A product manager bridges the gap between customer needs, company goals, and available resources to ensure that the product meets market demands and delivers business value.
Importance of Product Management in Modern Businesses
For businesses to stay competitive, they must respond quickly to market changes and customer feedback. Product management ensures that products evolve with market demands, making product managers the strategic masterminds behind profitable and scalable products. Their work directly influences customer satisfaction, revenue, and brand reputation.
Key Roles and Responsibilities of Product Managers
Product managers play a complex, dynamic role that touches many parts of a company. At the core, they are responsible for deeply understanding customer needs and market demands. This starts with researching customer issues, gathering feedback, and analyzing preferences through surveys, user data, and direct interactions. By understanding pain points, product managers ensure that each decision and feature resonates with target customers.
Beyond understanding customers, product managers are also tasked with crafting a clear product vision. This vision acts as the guiding “north star” for the entire product team. A product manager’s strategy aligns the product’s direction with the company’s broader goals, making sure that each new feature, update, or iteration contributes to the bigger picture.
To bring a product vision to life, product managers must prioritize features and manage a well-organized roadmap. Balancing what customers want with available resources, they decide which features to launch first, which to save for later, and which may need more development. This roadmap becomes a blueprint that helps everyone understand what’s next and why.
Collaboration across teams is also a big part of the role. Product managers work closely with engineers, designers, marketing teams, and sales. They make sure that each team’s efforts are aligned with the product’s objectives, so that when the product launches, it meets both technical and customer expectations.
Finally, product managers continuously monitor the product’s performance after launch. They track metrics, study customer feedback, and look for trends to spot areas for improvement. This cycle of gathering insights and refining the product helps keep it aligned with customer needs and competitive within the market.
Essential Skills for Product Managers
An effective product manager must bring a versatile skill set to the table:
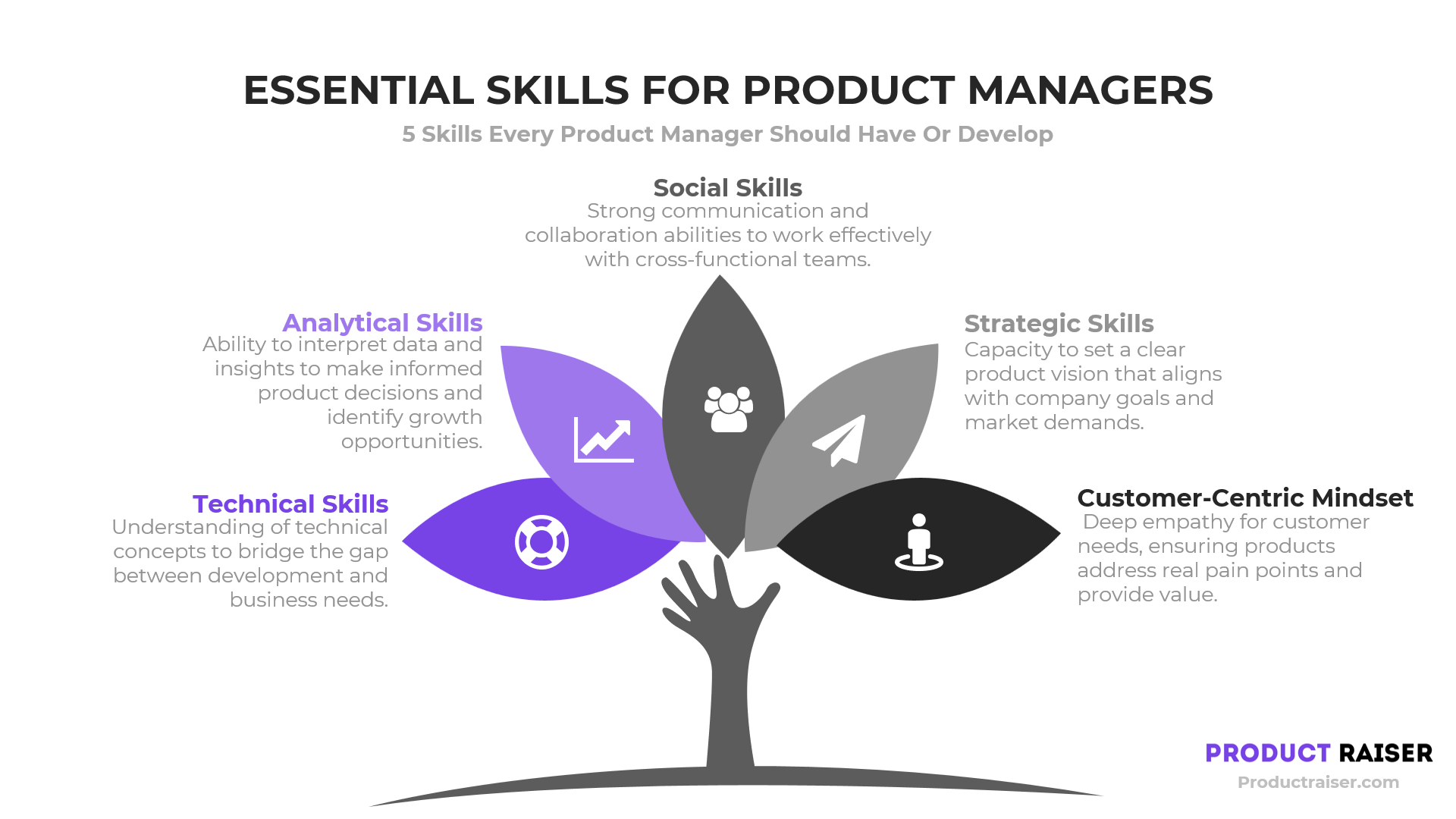
1. Technical Skills for Effective Product Management
Product managers don’t need to code, but a technical background helps them communicate effectively with development teams and understand the product’s capabilities and limitations.
2. Analytical and Problem-Solving Abilities
Product managers use data and Product Management KPIs to evaluate product performance and solve customer problems. Analytical skills are vital for interpreting customer feedback and making decisions that drive product growth.
3. Communication and Leadership Skills
Clear communication with teams and stakeholders is crucial for aligning everyone toward the product vision. Strong leadership motivates cross-functional teams to work effectively.
4. Strategic Thinking and Business Acumen
Product managers must understand the business landscape, competitive dynamics, and financial impact of product decisions. Strategic thinking ensures that each decision aligns with the broader company objectives.
5. Customer-Centric Mindset and Empathy
A great product manager always puts the customer first, understanding their needs, frustrations, and preferences to create a product that resonates.
Common Product Management Frameworks and Tools
Frameworks and tools help product managers streamline their processes:
The Video below provides a quick overview about a selection of tools and techniques which a used by many product managers.
1. Agile and Scrum Methodologies
Many product managers use agile and scrum frameworks to develop products iteratively, allowing for quick adjustments based on feedback and market changes.
2. Roadmapping and Prioritization Tools
Roadmapping tools like Aha!, ProductPlan, and Trello help product managers visualize their roadmap, set priorities, and track development progress. Experienced Product Managers use a Customer Persona to prioritize new features by guessing what customers might want most.
3. Product Lifecycle Management Tools
Product lifecycle management (PLM) tools enable product managers to track each phase of a product’s journey, ensuring that everything runs smoothly from development to market launch.
4. Data Analysis and Customer Feedback Tools
Analytics tools such as Google Analytics, Mixpanel, and Qualaroo help product managers understand user behavior, monitor performance, and gather feedback.
Product Manager Career Path and Growth Opportunities
Most product managers start their careers in entry-level roles such as Associate Product Manager (APM), where they learn the foundational skills of product management under the guidance of experienced product leads. In these roles, they often support senior product managers with tasks like feature prioritization, user research, and roadmap planning, gaining hands-on experience with the product lifecycle.
As they gain experience, product managers can advance to the role of Senior Product Manager. Here, they are typically responsible for managing entire products or product lines independently. In addition to defining the product vision and strategy, senior product managers lead cross-functional teams, oversee major launches, and are accountable for product success metrics.
The next step up the ladder is the Product Lead or Principal Product Manager. In these positions, the focus broadens, and product managers start managing a portfolio of products. They develop strategies across multiple teams, mentor junior PMs, and often work on scaling products for new markets or user segments.
For those who excel, the role of Head of Product or Vice President of Product awaits. This executive position involves leading entire product departments, making high-stakes strategic decisions, and aligning the product roadmap with the company’s overall vision. Heads of Product also shape the company’s product culture, handle budgets, and work directly with the C-suite to drive product-led growth across the organization.
You like it so far?
SIGN UP TO OUR NEWSLETTER FOR MORE INSIGHTS
Key Skills for Career Advancement in Product Management
Advancing in product management requires more than technical expertise; it’s also about cultivating soft skills and strategic vision that inspire and align teams. Here are some of the key skills that propel product managers to the top:
1. Leadership and Influence: Product managers must unify diverse teams toward a shared goal. Developing leadership skills, including conflict resolution and motivational techniques, empowers PMs to guide teams through challenges and celebrate successes.
2. Stakeholder Management: Senior PMs interact with various stakeholders, from engineers to executives. Being able to manage expectations, communicate transparently, and align different priorities is crucial to earning stakeholder trust and cooperation.
3. Strategic Vision: To reach higher-level roles, PMs need to sharpen their ability to set long-term product strategies that align with market opportunities and business objectives. This includes market analysis, competitive benchmarking, and understanding industry trends.
4. Data-Driven Decision-Making: PMs at every level need strong analytical abilities to interpret user data, identify trends, and make informed product decisions. This skill becomes even more critical as they advance, influencing high-stakes decisions that can affect entire product lines.
5. Adaptability and Customer Empathy: The best product managers are deeply customer-centric, continuously adapting products based on evolving user needs. Empathy enables them to foresee and address user pain points, creating products that genuinely solve customer problems and foster loyalty.
How to Become a Product Manager
While a bachelor’s degree in business, computer science, or engineering is common among product managers, those with backgrounds in psychology, marketing, or design also find success by offering unique perspectives on customer needs and product usability. Higher education, such as an MBA, is often advantageous, especially for those seeking roles at larger organizations or aiming for senior management positions.
Certifications like the Certified Scrum Product Owner (CSPO) and Product School’s Product Management Certificate provide structured learning and validate a PM’s knowledge of product methodologies. The Pragmatic Marketing Certification and AIPMM Certified Product Manager also offer specialized training in product management best practices, focusing on strategic decision-making and product lifecycle management.
Steps to Landing Your First Product Management Role
To start a career in product management, gaining relevant experience in areas like business analysis, marketing, or software development is key. Working on projects in these fields exposes you to customer research, project management, and user experience—all critical skills for product managers. As you grow, networking becomes invaluable; attending industry events, webinars, and joining communities like LinkedIn and ProductTank helps you connect with mentors who can offer guidance and job referrals.
Building a portfolio of projects also sets you apart. Even without a formal PM role, creating a small app or website demonstrates your problem-solving skills, ability to conduct customer research, and feature prioritization. Additionally, applying to Associate Product Manager (APM) programs, offered by companies like Google and Facebook, provides structured training and real-world experience, making it an excellent entry point into product management.
Salary and Job Outlook for Product Managers
Product manager salaries vary significantly based on industry, experience, and location. For example, PMs in tech-heavy regions like San Francisco or New York City often earn between $110,000 to $150,000 annually, while PMs in less competitive markets might see average salaries between $85,000 and $100,000.
Industry also plays a role: technology and finance sectors generally offer higher compensation for PMs due to the complex nature of their products and the high stakes involved. Additionally, senior roles such as Product Lead or Head of Product can command salaries well over $200,000, along with bonuses and stock options.
Job Market Demand and Long-Term Outlook
With the rapid growth of technology and digital products, the demand for skilled product managers is projected to continue rising. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics reports positive growth trends for product management-related roles, especially within tech, healthcare, and finance sectors. As companies recognize the strategic value product managers bring, roles are opening up even beyond tech, including industries like e-commerce, consumer goods, and manufacturing.
Product management is also evolving. With new advancements in artificial intelligence, data analytics, and automation, PMs with expertise in these areas will be highly sought after. The future for product managers remains promising, with strong job security and numerous opportunities for growth.
Should you become a Product Manager?
The journey to becoming a successful product manager is challenging but rewarding. This role offers a dynamic career with opportunities to impact a product’s success, shape customer experiences, and influence business growth. As industries continue to innovate, product managers with a blend of technical knowledge, strategic thinking, and customer empathy will find no shortage of exciting and lucrative career paths. With the right mix of experience, skills, and networking, aspiring PMs can not only break into the field but also advance to senior roles, enjoying both financial rewards and professional satisfaction.
As a Prodcut Manager it’s very important to stay up to date with the newest trends and news in the industry! Subscribe to our newsletter for more information, templates, expert tips, and the latest tools to help you to start and grow in product management!
Newsletter
MORE TIPS, TEMPLATES AND EXCLUSIVE INSIGHTS
Stay Ahead Of Others With Our Newest Articles
Best Product Ideation Frameworks and Processes
Learn key steps, agile techniques, and frameworks to master product ideation with real-life examples and best practices!
10 Essential Product Market Fit Survey Questions
Discover essential survey questions to understand customer pain points and validate product-market fit for your product.
Feature Adoption Rate | Benchmark & Case Studies
Discover what a good feature adoption rate is, how to measure it, and benchmarks to target. Learn the formula and examples from top companies.
Enhance A/B Testing Accuracy with Re-Randomization for Product Management
Boost A/B test accuracy in product management with re-randomization., Reduce bias, and gain reliable insights for data-driven decisions.
16 Key Activities to Validate Product-Market Fit During MVP-Phase
Discover key activities to validate product-market fit during MVP. Learn hands-on strategies to refine your product, meet user needs, and drive growth.
Top 10 Best Product Management Books for PMs
Learn how to optimize listings, gain reviews, and boost sales on Amazon in 2024.